Theory
The surface of a solid has a tendency to attract and to retain molecules of other species (gas or liquids) with which such surfaces come in contact. This phenomenon of surfaces is termed as adsorption.
Differences between Adsorption, Absorption and Sorption. Adsorption is a surface phenomenon whereas absorption is a bulk phenomenon in which the substance assimilated is uniformly distributed throughout the body of a solid or liquid to form a solution or a compound.

The material on the surface of which adsorption takes place is called the adsorbent and the substance adsorbed is called the adsorbate. The common surface separating two phases, where the adsorbed molecule concentrates is referred to as the interface. The large the surface area of the adsorbent, the more the adsorption. Due to this reason colloids are good adsorbents due to their high surface area per unit mass although they have very small dimensions.
CHARACTERISTICS OF ADSORPTION :
- Adsorption is a spontaneous process and takes place in no time.
- The phenomenon of adsorption can occur at all surfaces and five types of interfaces can exist: gas -solid, liquid-solid, liquid-liquid, solid-solid and gas-gas.
- It is accompanied by a decrease in the free energy of the system, i.e., ΔG. The adsorption will continue to such an extent that ΔG continues to be negative.
Factors on which Adsorption depends :
The phenomenon of adsorption of gases by solids depends upon the following factors:
- Nature of adsorbent and adsorbate : The amount of the gas adsorbed depends upon the nature of the adsorbent and the gas (adsorbate) which is to be adsorbed.
- Surface area of the adsorbent : Larger the surface area of the adsorbent, the large will be the extent of adsorption under
given conditions of temperature and pressure. - The partial pressure of the gas in the phase : The magnitude of adsorption decreases with the decrease in pressure and vice-versa.
- Effect of temperature : The decrease in temperature will increase the adsorption and viceversa.
There are two types of adsorptions: Physisorption and Chemisorption

MCQ
Short Answer
p-Toluidine, a yellow liquid used in the manufacture of dyes, is only slightly soluble in water. The surface tension of p-toluidine was measured at various concentrations at 25oC (298 K) and the results were plotted. The slope, dγ/dc, of the line at c = 5 × 10-3 g/cm3 was found to be 32,800 cm3/sec2. Using the Gibbs adsorption equation, compute the excess surface concentration in mole/cm2 and in g/cm2. The molecular weight of p-toluidine is 107.15 g/mole.
Solution:
slope = ![]() = 32800 g cm3/sec2
= 32800 g cm3/sec2
c = 5 x 10-3 g/cm3
R = gas constant = 8.314 x 107 erg K-1 mol-1
T = temperature = 298 K
excess surface concentration = ![]()
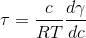
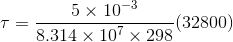
= 6.6 x 10-9 mole/cm2
So, excess surface concentration = 6.6 x 10-9 mole/cm2
To convert the units into g/cm2 =>
1 mole of p-toluidine = 107.15 g
So, excess surface concentration = 6.6 x 10-9 x 107.15 g/cm2 = 707 x 10-9 g/cm2 = 7.07x 10-7 g/cm2
Quick Link
